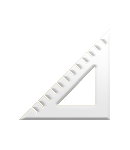
How to Order Custom Magnets
The 4-step process of ordering custom manufactured magnets is easier than ever.
Looking For Bespoke Magnets?
The process of ordering custom manufactured magnets is straight forward. In most cases, customers come to us with shape, size and pull force (KG) requirements.
If your magnet will be exposed to high temperatures or harsh conditions, other factors like coercivity and coating need to be considered. If you’re unsure about anything, everything will be explained below.
What Can You Customise?
Types of Magnets
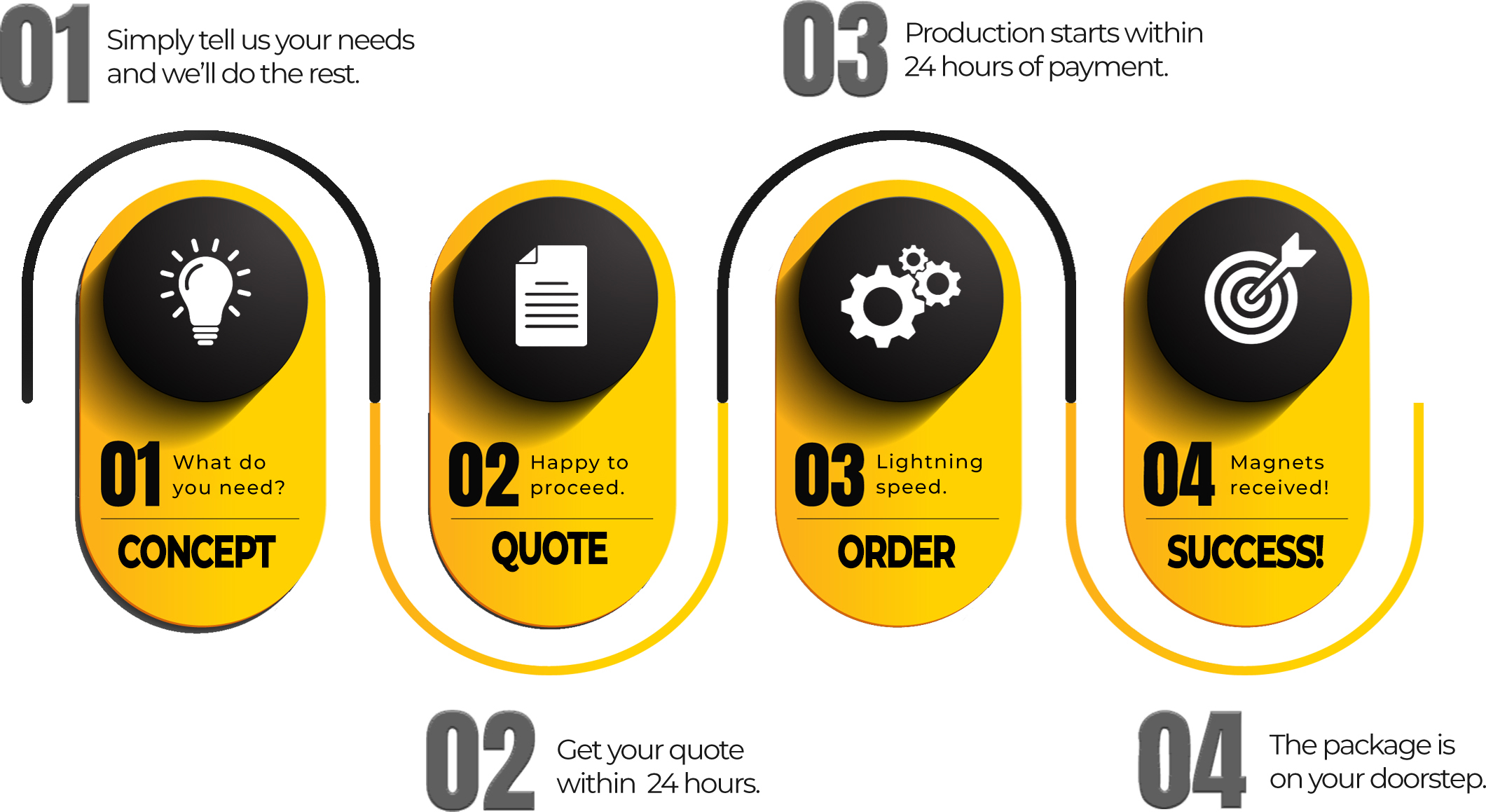
There are 4 main types of magnets that each have their own unique properties.
Neodymium magnets are the most popular since they are the most magnetically powerful permanent magnets available. They can also be produced in any shape and size, making them ideal for a huge range of applications.
Samarium cobalt (or SmCo) is a rare earth magnets which is the second strongest permanent magnet available. SmCo magnets are usually used for their ability to operate in high temperatures.
AlNiCo is an alloy made from aluminium, nickel and cobalt – these are not as magnetically powerful as neodymium or samarium cobalt, but they are the superior magnet to extreme temperatures and other demagnetisation forces.
Ceramic or ferrite magnets have weaker levels of magnetism than rare earth magnets but they are much more cost effective and simple to mass produce.
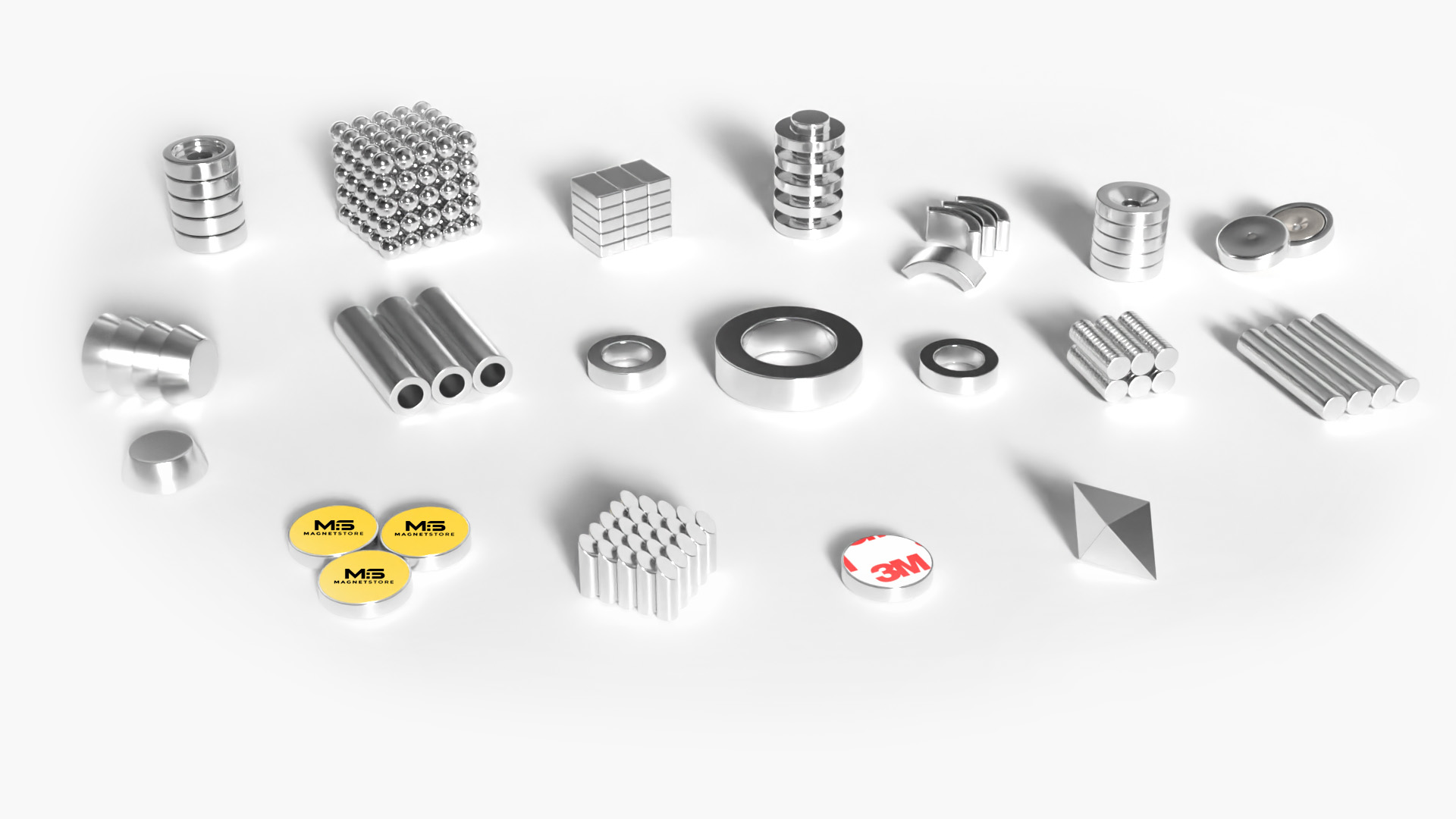

Magnet Shapes and Sizes
The most common shapes of magnets are disc magnets, block magnets, cylinder magnets, countersunk magnets, ring magnets, arc magnnets and pot magnets.
Each shape has it’s own unique advantages for different applications. The great news about our service is that you choose the exact shape and size dimensions that works best for your project.
What are Magnets Grades?
Magnets have various grades which offer different strengths of magnetism, cost and resistance to demagnetisation forces. For example, neodymium grades range from N35 to N55. N35 magnets have the lowest magnetism and N55 magnets have the highest.
This means you’ll need a higher grade if you require more magnetism or power. We find N42 magnets are the perfect balance between cost and performance, however, other grades are also available such as N35, N38, N40, N45, N48, N52 and N55.

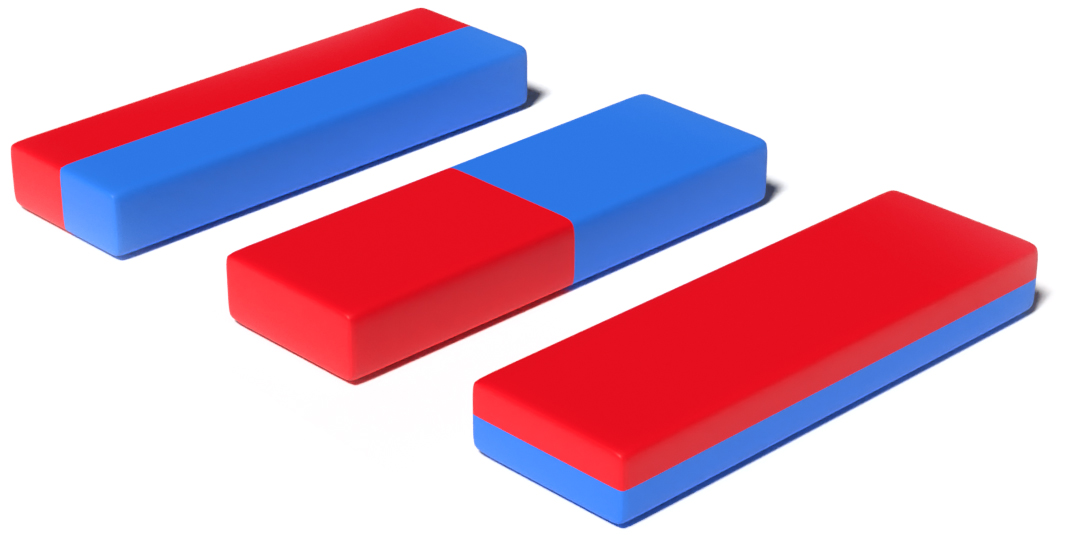
Magnetisation Direction
Most magnets are axially magnetised which means they are magnetised through the length of the magnet. For example, this kind of magnetisation provides the largest surface area for holding in disc and block magnets. There are other less common types of magnetisation directions available for specialist applications. These magnetisation directions are called diametrical, lateral multi-poles, radial and segmental.
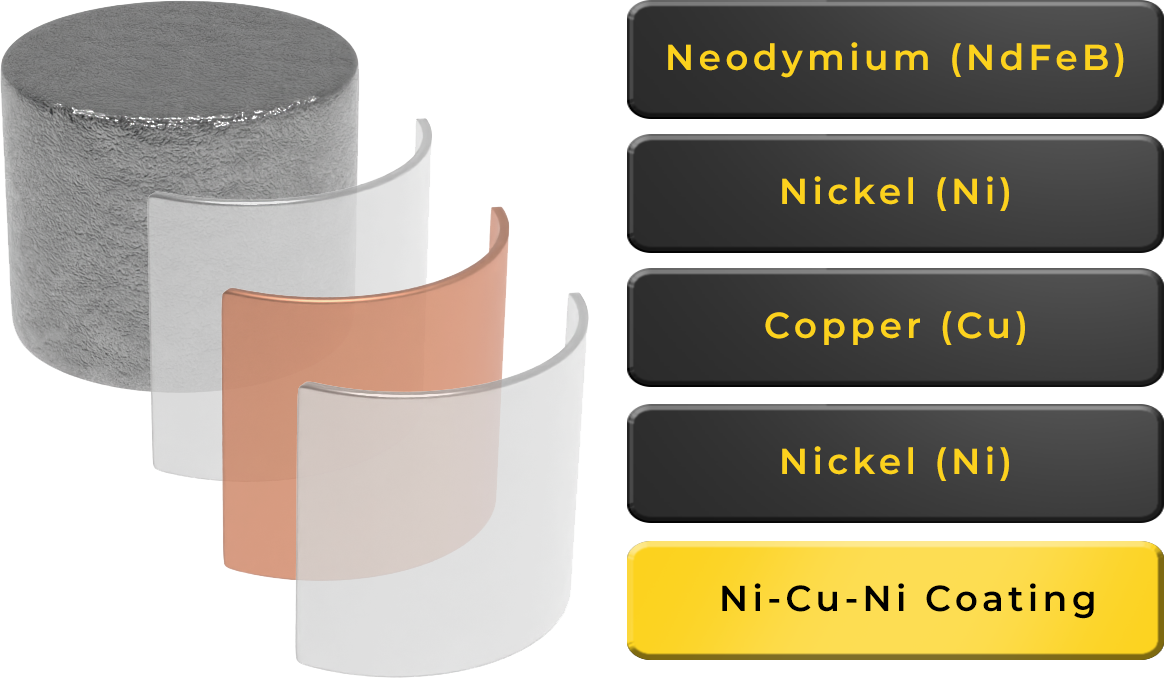
Permanent Magnets and Coating
Neodymium magnets are most commonly produced with a triple layer coating of Ni-Cu-Ni (Nickel, Copper, Nickel) to prevent signs of corrosion. This gives the magnet a metallic silver colour and is great for indoor/dry use. Ni-Cu-Ni coating doesn’t solve all corrosion problems as they can still corrode in harsh, wet and humid conditions. This means if your magnet will be exposed to these harsh conditions, other coating options may need to be considered.
Samarium cobalt magnets (SmCo), alnico magnets and ferrite magnets do not usually need a protective coating because the materials do not easily corrode.

Operating Temperatures (Coercivity)
Extreme temperatures, magnetic pulses and kinetic force can destroy the magnetism of permanent magnets. Neodymium magnets have a standard operating temperature of 80 °C which is perfect for most applications.
For more challenging environments, we can produce neodymium magnets that can withstand temperatures up to 220 °C. We can also produce SmCo, Alnico and ferrite magnets which can withstand much higher levels of demagnetisation forces.